We have to maximize
z = 9x + 3 y
subject to the constraints
2x + 3 y ≤ 13
2x + y ≤ 5
x, y ≥ 0
Consider a set of rectangular cartesian axes OXY in the plane.
It is clear that any point which satisfies x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0 lies in the first quadrant.
Let us draw the graph of 2x + 3y = 13
For x = 0, 3y = 13 ![]()
For y = 0, 2x = 13 ![]()
![]()
Again we draw the graph of 2x + y = 5
For x = 0, y = 5
For y = 0, 2x = 5 ![]()
![]()

Since feasible region satisfies all the constraints.![]() OCEB in the feasibe region. The corner points are O(0, 0),
OCEB in the feasibe region. The corner points are O(0, 0), ![]()
At O(0, 0), z = 9(0) + 3(0) = 0+ 0 = 0
At ![]()
At ![]()
![]()
![]()
We are to maximize
z = 4x + 7y
subject to the constraints
x + 2y ≤ 20
x + y ≤ 15
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Consider a set of rectangular cartesian axes OXY in the plane.
It is clear that any point which satisfies x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 lies in the first quadrant.
Now we draw the graph of line
x + 2y = 20.
For x = 0, 2y = 20 or y = 10
For y = 0, x = 20
∴ line meets OX in A (20, 0) and OY in L (0, 10).
Let us draw the graphs of line
x + y = 15.
For x = 0, y = 15
For y = 0, x = 15
∴ line meets OX in B (15, 0) and OY in M (0, 15).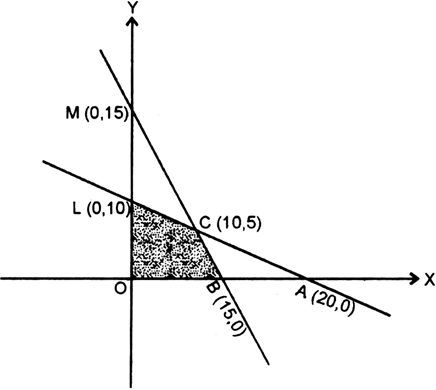
Since feasible region is the region which satisfies all the constraints
∴ OBCL is the feasible region, which is bounded.
The corner points are O (0, 0), B (15, 0), C (10, 5), L (0, 10)
At O (0, 0), z = 0 + 0 = 0
At B (15, 0), z = 4 (15) + 7 (0) = 60 + 0 = 60
At C(10, 5), z = 4 (10) + 7 (5) = 40 + 35 = 75
At L (0, 10), z = 4 (0) + 7 (10) = 0 + 70 = 70
∴ maximum value = 75 at the point (10, 5).
We are to maximise
Z = 4x + y
subject to the constraints
x + y ≤ 50
3x + y ≤ 90
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Consider a set of rectangular cartesian axes OXY in the plane.
It is clear that any point which satisfies x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 lies in the first quadrant.
Now we draw the graph of the line x + y = 50
For x = 0, y = 50
For y = 0, x = 50
∴ line meets OX in A(50, 0) and OY in L(0, 50)
Let us draw the graph of line 3 x + y = 90
For x = 0, y = 90
For y = 0, 3x = 90 or x = 30
∴ line meets OX in B(30, 0) and OY in M(0, 90).
Since feasible region is the region which satisfies all the constraints.
∴ OBCL is the feasible region, which is bounded.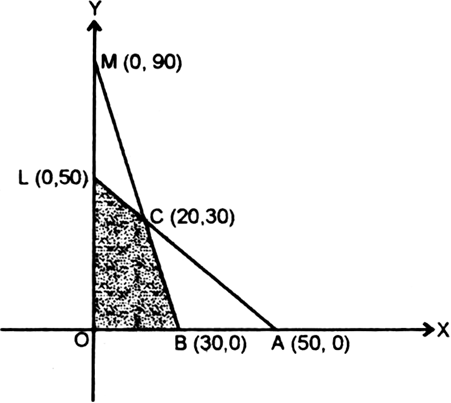
The comer points are
O(0, 0), B(30, 0), C(20, 30), L(0, 50)
At O(0, 0), Z = 0 + 0 = 0
At B(30, 0), Z = 120 + 0 = 120
At C(20, 30), Z = 80 + 30 = 110
At L(0, 50), Z = 0 + 50 = 50
∴ maximum value = 120 at the point (30, 0).
Tips: -
Note: Coordinates of C can be found by two methods:
Method I: Draw the graph of inequalities on the graph paper. So coordinates of C can be determined.
Method II: Solve the two equation x + y = 50, 3x + y = 90 by any method to find coordinates of C.
We are to maximize
z = 11x + 5y
subject to the constraints
3x + 2y ≤ 25
x + y ≤ 10
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Consider a set of rectangular cartesian axes OXY in the plane.
It is clear that any point which satisfies x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 lies in the first quadrant.
Now we draw the graph of 3x + 2y = 25
For x = 0, 2y = 25 or ![]()
For y = 0, 3x = 25 or ![]()
![]()
![]()
Again we draw the graph of x + y = 10
For x = 0, y = 10
For y = 0, x = 10
∴ line meets OX in B (10, 0) and OY in M (0, 10).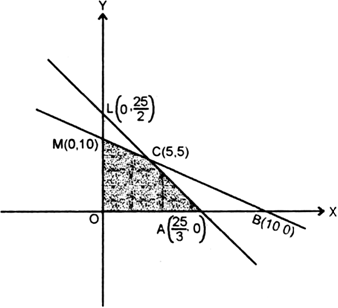
Since feasible region is the region which satisfies all the constraints
∴ OACM is the feasible region and corner points are![]()
At ![]()
At ![]()
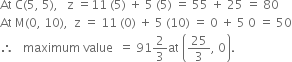
We are to maximize
f = x + 2y
subject to the constraints
2x + 3 y ≤ 6
x + 4 y ≤ 4
x, y ≥ 0
Consider a set of rectangular cartesian axes OXY in the plane.
It is clear that any point which satisfies x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 lies in the first quadrant.
Now we draw the graph of the line 2 x + 3 y = 6.
For x = 0, 3 y = 6, or y = 2
For y = 0, 2 x = 6, or x = 3
∴ line meets OX in A (3, 0) and OY in L (0, 2)
Let us draw the graph of line x + 4 y = 4
For x = 0, 4 y = 4, or y = 1
For y = 0, x = 4
∴ line meets OX in B (4, 0) and OY in M (0, 1)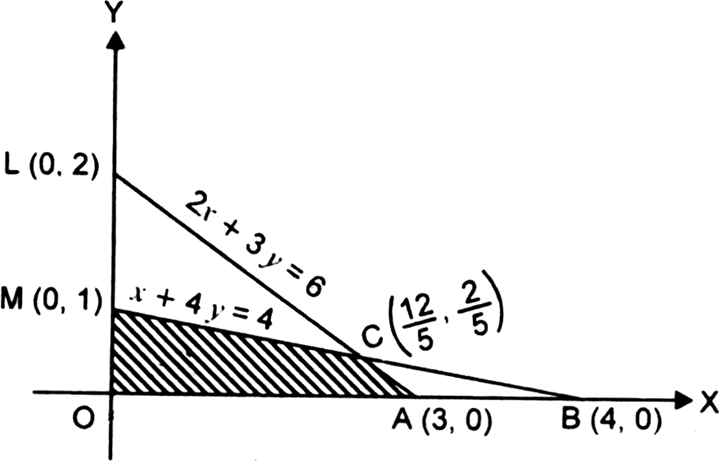
Since feasible region is the region which satisfies all the constraints
∴ OACM is the feasible region. The comer points are
![]()
At ![]()
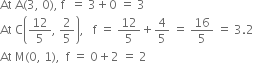
![]()
