
Show that the points (2, 3, 4), (–1, –2, 1), (5, 8, 7) are collinear.
Find the cartesian equation of the line which passes through the point (-2, 4, -5) and is parallel to the line given by ![]()
Direction-ratios of the line ![]()
∴ equation of the line through (–2, 4, –5) and having direction ratios 3, 5, 6 are![]()
Let P (1, –1, 2), Q (3, 4, –2), R (0, 3, 2) and S (3, 5, 6) be given points.
Direction ratios of RS are 3 - 0, 5 - 3, 6 - 2 i.e. 3, 2, 4.
∴ direction cosines of RS are
![]()
i.e., ![]()
Projection of PQ on RS
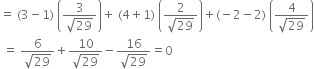
∴ PQ is perpendicular to RS
Hence the result.
