Lichen is usually cited as an example of ‘symbiosis’ in plants where an algal and a fungal species live together for their mutual benefit. Which of the following will happen if algal and fungal partners are separated from
each other?
a. Both will survive and grow normally and independent from each other.
b. Both will die
c. Algal component will survive while the fungal component will die.
d. Fungal component will survive while algal partner will die.
Symbiosis is the term used for the relationship in which two organisms get benefit from each other.
Lichen is a symbiotic relationship between algae and fungus.But the symbiotic relationship is an obligate one. This means that the organisms require the symbiotic relationship in order to survive.
The algae and fungus are mutually dependent on each other. The fungus is the only source of water and nutrients for the algae.
Algae is the only source of food to the fungus. There are no alternative means for meeting the basic needs. Thus, If the two are sperated both will die because they will not be able to fulfil the requirements in the absence of the other.
Thus option b is true. Both will die.
Bryophytes have the following economic importance.
i. Some mosses provide food for herbaceous mammals, birds.
ii. Some species like Sphagnum provide peat that is used as a fuel and a packing material.
iii. Mosses and lichens decompose rocks and help in the formation of soil.
iv. Mosses reduce soil erosion as they form dense mats on the ground.Briefly, explain the pattern of lifecycle followed by
a. All bryophytes
b. All pteridophytes
The bryophytes and pteridophytes both follow a Haplo-diplontic lifecycle.
Bryophytes - The haploid generation represents a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, thalloid or erect phase. The haploid phase alternates with the shortlived multicellular sporophyte totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte for its anchorage and nutrition.
Pteridophyte - The diploid sporophyte is represented by a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, vascular plant body. It alternates with multicellular,
saprophytic/autotrophic, independent but short-lived haploid gametophyte.
Explain why sexual reproduction in angiosperms is said to take place through double fertilization and triple fusion.
In angiosperms, one male gamete fuses with the female gamete. In addition to this, another male gamete fuses with the secondary nucleus. Fusion between male and female gametes result in the formation of zygote. While the fusion of the male gamete and the secondary nucleus forms the primary endosperm nucleus or (PEN).
Since two instances of fusion of nuclei take place hence the phenomenon is known as Double fertilisation.
The phenomenon is called triple fusion as the male gamete fuses with the secondary nucleus having two polar nuclei and results in the formation of endosperm which has 3n chromosome.
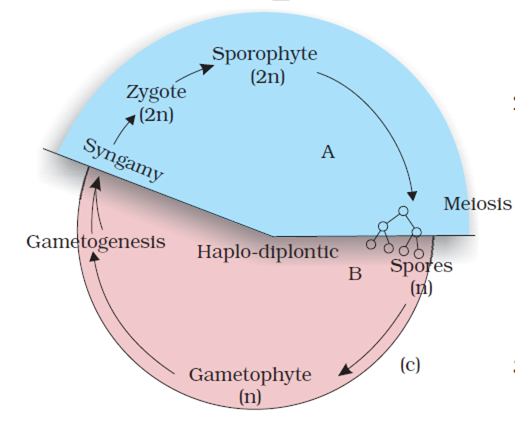
With the help of a schematic diagram describe the haplo-diptontic life cycle pattern in plants
In a sexually reproducing plant, there is an alternation of generation between a haploid and a diploid phase of plant bodies.
The haploid plant body is termed gametophyte while the diploid plant body is called sporophyte.
The gametophyte produces gametes by mitosis while the haploid spores are produced by sporophyte following meiosis (reduction division). Two gametes fuse together to produce a zygote which develops into the diploid sporophyte. In a haplodiplontic life cycle pattern, such as in bryophyta or pteridophyta both the phases of life are multicellular.
However, in bryophytes, the gametophytes are small, photosynthetic, independent and represent dominant phase. The partly or totally dependent, the sporophyte is physically attached to the gametophyte. The (n) spores dispersed by sporophyte germinate into individual gametophytic plants.
In pteridophytes, the 2n (diploid) phase is dominant, well organized, independent while the haploid phase though also free-living and independent is short lived and photosynthetic.
In both of these groups of plants the mobile male gametes, antherozoid produced by sex organ antheridium, travel to archegonium (bearing an egg cell) via the medium of water. The egg cell is nonmotile. The reproduction is oogamous.