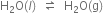Reversible reactions: Reactions which proceed in both directions are called reversible reactions. In a reversible reaction, the reactants are changed into products and simultaneously the products are changed into reactants. A reversible reaction is shown by using two half arrows in opposite direction  . In a reversible reaction, the reaction proceeding from left to right (reactants that give the products) is called forward reaction. The reaction proceeding from right to left (products that give back the reactants) is called a backwards reaction. The reversible reaction generally proceeds in a closed vessel. This prevents the escape of the products. Example of reversible reaction are:
. In a reversible reaction, the reaction proceeding from left to right (reactants that give the products) is called forward reaction. The reaction proceeding from right to left (products that give back the reactants) is called a backwards reaction. The reversible reaction generally proceeds in a closed vessel. This prevents the escape of the products. Example of reversible reaction are:
Irreversible reactions: A chemical reaction is said to be irreversible if reactants are changed into products (proceeds only in the forward direction) but the products do not combine to form the reactants. These reactions are indicated by a single arrow  in a chemical equation. Examples of irreversible reactions are:
in a chemical equation. Examples of irreversible reactions are:
(i) Burning of magnesium

(ii) Decomposition of potassium chlorate.
(iii) The reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water vapours. 

(i) In case of liquid  gas equilibrium, the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes constant at a given temperature.
gas equilibrium, the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes constant at a given temperature.
(ii) In case of solid  solution equilibrium, the concentration of solute in solution becomes constant at a given temperature.
solution equilibrium, the concentration of solute in solution becomes constant at a given temperature.
(iii) In the case of gas  solution equilibrium, the pressure of the gas above liquid becomes constant at a given temperature.
solution equilibrium, the pressure of the gas above liquid becomes constant at a given temperature.
(iv) In the case of solid  liquid equilibrium, there is only one temperature (melting point) at which two phases can co-exist i.e. temperature remains constant at a given pressure.
liquid equilibrium, there is only one temperature (melting point) at which two phases can co-exist i.e. temperature remains constant at a given pressure.
Hence the common characteristics of physical equilibrium are:
1. Equilibrium can be established only in case of a closed system.
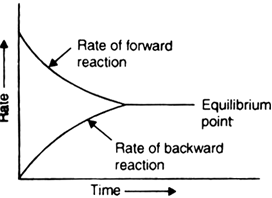
2. The equilibrium is dynamic in nature i.e. the process does not stop after the establishment of equilibrium but the rate of the forward reaction becomes equal to the rate of backward reaction.
3. The measurable properties of the system such as melting point, boiling point, vapour pressure and solubility remain constant since the concentration of the substances remains constant.
4. When equilibrium is attained there exists an expression involving the concentration of reacting substances which acquire a constant value at a given temperature.
5. In the case of a gas dissolving in a liquid, the increase of pressure always increases the solubility of the gas in the liquid.