Discuss measures for the control of CO pollution.
The main source of CO pollution due to human activity is the use of internal combustion engine in the automobiles. These engines emit a mixture of CO, NOx, hydrocarbons and particulates. The following measures may be adopted to check CO pollution:
1. By using antipollution catalysts: Automobile exhaust is treated with the antipollution catalyst before discharging into the atmosphere. It consists of two steps:
(a) In the first step, oxides of nitrogen are reduced to ammonia and nitrogen by using finely divided platinum. The quantity of NH3 is made minimum through suitable conditions.
(b) In the second step, air or oxygen is introduced to oxidise CO and hydrocarbons into CO2 and H2O in the presence of finely divided Pt catalyst. In modern automobiles, catalytic exhaust reactors are used in which excess air is pumped into the exhaust gas and the mixture is passed through a catalytic converter in the exhaust system.
2. By modification of internal combustion engines: Internal combustion engines are modified to reduce the amount of pollutants formed during fuel combustion. The presence of excess air ensures complete combustion of CO and hydrocarbons to CO2 and water.
Automobile carburettors are adjusted and cleaned regularly to the proper fuel-air ratios.
3. By using substitute fuel: Instead of gasoline, the use of CNG (Condensed natural gas) and LNG (Liquefied natural gas) have been used as these are pollution-free fuels.
Discuss air pollution caused by oxides of nitrogen.
Or
What are the principal environmental effects of NO2?
Or
Name the oxide of nitrogen present in the atmosphere. What are the sources and sinks of NOx?
A number of oxides of nitrogen such as NO, N2O, NO2, N2O3 and N2O5 are introduced into the atmosphere due to the natural sources and due to human activity. NO and NO2 are considered as pollutants and denoted by the general formula NOx.
The source of NOx. Nitric oxide (NO) is a colourless gas and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is reddish brown gas having a pungent smell and is suffocating in nature.
(i) Natural sources: Natural bacterial action is the only natural source which discharges NOX mainly in the form of NO into the atmosphere in large quantity. Lightning discharge also results in the combination of N2 and O2 to form NO.
(ii) Man-made sources: The major man-made sources of NOx are combustion of coal, oil, natural gas and gasoline. The basic reactions are: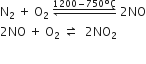
(iii) Chemical industries as a source: Chemical industries like sulphuric acid and nitric acid industries produce NOx as by-products which are discharged into the air.
Sinks of NOx: NOx (i.e. NO and NO2) in the atmosphere are converted into nitric acid through the following reactions in which ozone also takes part: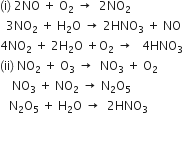
Nitric acid acts as a temporary sink and comes down in the form of acid rain or precipitates as nitrate salts after reacting with bases such as ammonia, lime etc.
Harmful effects of NOx pollution:
(i) Nitric oxide binds to haemoglobin and decreases oxygen transport efficiency of blood.
(ii) Acid rain (HNO3) can cause the pH of the water to drop to 4 or 5. This can affect vegetation and building materials.
(iii) The sunlight reacts with nitrogen dioxide to produce highly active oxygen atoms.
The active oxygen immediately reacts with traces of hydrocarbons in the air and produces irritates called photochemical smog. This is a health hazard.
(iv) Oxides of nitrogen have a harmful effect on nylon, rayon and cotton yarns and also cause of fading of dyes used for textiles.
(v) Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) results in respiratory problems in human beings and leads to bronchitis.
Discuss sources and sinks of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Or
Discuss the role of CO2 as a pollutant.
Or
Carbon dioxide is inert and harmless gas, yet it is considered to be a serious pollutant. Explain.
Source of CO2: The main sources of CO2 are:
(i) Complete combustion of fuels and carbon compounds and carbonates. 
(ii) Auto-exhaust and many industrial processes also produce a lot of carbon dioxide.
(iii) Carbon dioxide is also produced by the biological decay of plants.
Sinks of CO2:
(i) The most important sink of CO2 is the ocean; ocean contains most of the dissolved CO2 in the form of carbonates, bicarbonates and organic compounds.
(ii) Another sink of CO2 is the living green plants where photosynthesis process occurs which results in the removal of CO2 in the atmosphere.
CO2 as a pollutant.
The increasing concentration of CO2 (presently 325 ppm) can lead to increase in the earth’s temperature i.e. green house effect occurs. A slight increase in the earth’s temperature can cause havoc in times of change in world climate, melting of glaciers, flooding of the coastal plains and change in biological activity of the ocean.
Plants maintain a balance in the atmospheric CO2 level by using it in photosynthesis
Control of CO2 pollution:
CO2 pollution can be controlled by using following steps:
(i) The release of CO2 from various industrial processes should be controlled.
(ii) The production of CO2 from vehicles exhaust should be checked.
(iii) To adjust the balance of CO2 in the atmosphere, the main sink of CO2 i.e. forests should be developed.
What do you understand by air pollution? Discuss the types of air pollutants.
Air pollution is defined as the addition of undesirable materials into the atmosphere either due to the natural phenomenon or due to human activity on the earth which adversely affects the quality of air and hence causing harm to humans, other animals, vegetation and materials. The chemical substance causing pollution is called air pollutant. About 90% of air pollution problems are caused by the pollutants such as carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, sulphuric acid, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds and suspended particulate matter.
The natural sources of air pollution are volcanic eruptions, vegetable decay, forest fires (caused by lightning), evaporation of volatile organic compounds from leaves and wind erosion of soil.
Man made pollutants are carbon dioxide (CO2), oxides of nitrogen (NO, NO2), sulphur dioxide (CO2), hydrocarbons, aerosols etc.
Air is also polluted by burning of fuels (coal, oil, gasoline, etc.) in power and industrial plants and in motor vehicles.
Types of air pollutants: There are two types of air pollutants:
(i) Primary air pollutants
(ii) Secondary air pollutants
(i) Primary air pollutants: A primary air pollutant is a harmful chemical substance that directly enters the air as a result of natural events or human activities. For example carbon oxides (CO and CO2), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2), sulphur oxides (SO2), hydrocarbons and suspended particulate matter.
(ii) Secondary air pollutants: A secondary air pollutant is a harmful material which is formed in the air due to a chemical reaction between two or more air components or a primary pollutant and one or more air components in the atmosphere. For example sulphur dioxide (primary pollutant) reacts with oxygen gas (in the atmosphere) to form secondary pollutant sulphur trioxide (SO3).
Sulphur trioxide formed may react with water vapours in air to form sulphuric acid.
Sulphuric acid is also a secondary pollutant. Other secondary pollutants are SO3, H2SO4, NO2, HNO3, H2O2 etc.
Discuss pollution caused by CO.
Or
What are different sources of CO pollution? What are the effects of continuous exposure to CO on human beings?
Carbon monoxide is a colourless and tasteless gas and is not soluble in water. It is formed in a number of ways:
(i) By the incomplete combustion of fuels and substances containing carbon.
(ii) By the reaction between CO2 and carbon at high temperature particularly in a blast furnace.
(iii) By the dissociation of carbon dioxide at high temperature.
(iv) Some natural processes like volcanic activity, natural gas emission, seed germination, electrical discharge during storm etc release some amount of CO into the atmosphere.
(v) Carbon monoxide is also released by the combustion of diesel, petrol etc. in the engines of automobiles and as a result of certain industrial processes.
Harmful effects:
(i) Effect of CO on human health: Carbon monoxide when inhaled passes through the lungs into the blood where it reacts with haemoglobin (Hb) of the red blood corpuscles (RBC) to form a stable compound known as carboxy haemoglobin (Hb – CO).
The latter is not in a position to transport the inhaled oxygen to various parts of the body. This will cause suffocation and ultimately lead to death.
(ii) Effect of CO on plants: A high concentration of carbon monoxide will harmfully affect the plants causing leaf drop, a decrease in leaf size and premature ageing of the plants.
