In the figure, m∠DBC = 58°. BD is the diameter of the circle. Calculate:
(i) m∠BDC
(ii) m∠BEC
(iii) m∠BAC

Consider the followiong figure:

(i) Given that BD is a diameter of the circle.
The angle in a semi circle is a right angle.
So, we can write,
Also, given that
In BDC, by angle sum property, we have
(ii) is cyclic quadrilateral.
we know that, opposite angles are supplementary
(iii) Angles in the same segment are equal.
In the figure given below 'O' is the centre of the circle. If QR = OP and ∠ORP = 20°. Find the value of 'x' giving reasons.
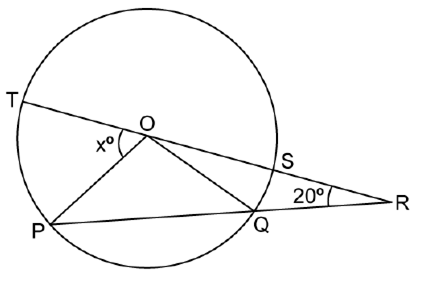
Now,
OP = QR .........GIVEN
So, OP = OT = OQ = QR
RQ = QO
Now
Now,
The given figure represents a kite with a circular and a semicircular motifs stuck on it. The radius of a circle is 2.5 cm and the semicircle is 2 cm. If diagonals AC and BD are of lengths 12 cm and 8 cm respectively, find the area of the:
(i) Shaded part. Give your answer correct to the nearest whole number.
(ii) Unshaded part.

(i) Area of the shaded part = Area of the circle + area of the semicircle
Area of the unshaded part = Area of the kite - Area of the shaded pa
= 48 - 26
= 22 cm2.
In the figure given, O is the centre of the circle. DAE = 70o, Find giving suitable reasons the measure of:
(i) BCD
(ii) BOD
(iii) OBD
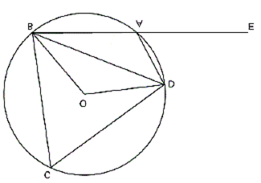
Since ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral, sum of the measures of the opposite angles are supplementary.
By Angle Sum property,
