(a) Explain the DDT resistance of mosquitoes to the pesticide.
(b) What are the symptoms of Diabetes mellitus?
(c) Define :
(i) Gene pool
(ii) Genetic Erosion.
(a) Repeated use of the same class of pesticides like DDT can cause undesirable changes in the gene pool of a mosquito leading to another form of artificial selection, pesticide resistance. When a pesticide is first used, a small proportion of the mosquitoes population may survive exposure to the material due to their distinct genetic makeup. These individuals pass along the genes for resistance to the next generation. Subsequent uses of the pesticide increase the proportion of less-susceptible individuals in the population. Through this process of selection, the population gradually develops resistance to the pesticide. Worldwide,many species of insectshave developed some level of pesticide resistance.
(b) Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus : The symptoms of diabetes mellitus are increased blood glucose level, excessive urination, passing out of glucose in the urine, excessive appetite, loss of weight, general weakness and thirst.
(c) (i) Gene Pool : It is the sum total varieties of all the genes and their alleles found in all the individuals of a population of species.
(ii) Genetic Erosion : The loss of genes from the gene pool is termed as genetic erosion. It takes place due to deforestation, shifting cultivation, urban expansion, damage to ecosystem and adoption of certain genetically uniform crop plants.(a) Describe Lederberg’s Replica Plating experiment to show the genetic basis of adaptation.
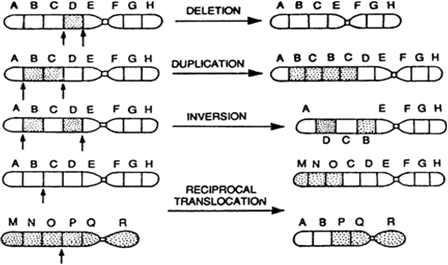
(b) Give an account of chromosomal aberrations (mutations).
(c) What is a pacemaker? 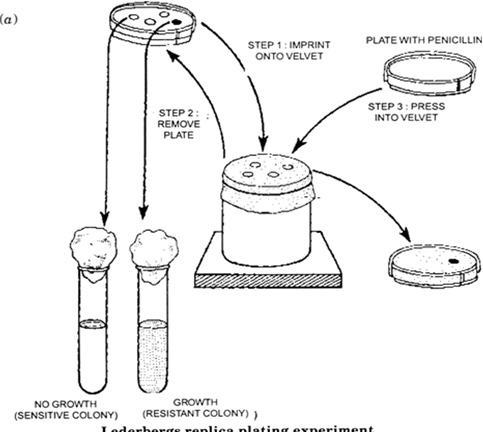
Lederberg’s Replica Plating Experiment: Joshua Lederberg and Esther Lederberg performed an experiment on bacteria to demonstrate the genetic basis of a particular adaptation. They obtained a ‘master plate’ of bacterial culture by inoculating a dilute suspension of bacteria on an agar plate. After a certain period, the master plate was found to contain several bacterial colonies. Each colony represented a clone that has originated from a single bacterial cell as a result of repeated divisions. They prepared many replicas of the master plate on new agar plates. After that, they tried to grow bacteria on replica plates with an antibiotic (e.g., penicillin). Most colonies of the master plate failed to grow on replica plates having antibiotic. Only a few colonies that could be formed were found to be resistant to penicillin. It means that certain bacteria have acquired an ability to survive and grow in a new environment. This mutant strain of bacteria has adapted. According to Darwinism, the original suspension of bacterial cells contained few mutant bacteria which had mutant genes that enabled them to survive the effect of penicillin and form colonies.
(b) Chromosomal aberrations: The alteration in the number of chromosomes or parts of chromosomes results in the changes in the traits of the organism. This is known as a chromosomal aberration or chromosomal mutation. The structural changes in the chromosomes may occur due to the effect of radiations, chemicals, drugs and even some viral infections.
In general, the changes in the structure of chromosome occur during the cell division when homologous chromosomes pair up and crossing over takes place.
If chromosome breaks and the broken parts do not reattach then the pieces may be lost. This situation results in some serious kind of chromosomal mutation. In such cases, the genes present on the missed fragment of the chromosome are not available to the off-springs. This is known as deletion.
(c) Pacemaker: It is an artificial device which is used to maintain the pace of the heart in a cardiac patient. The pacemaker generates heart beat at a normal rate. Nowadays, pacemakers are used widely throughout the world. It has proved to be a boon to the heart patients. It is implemented when the heart rate of the patient falls below 30-40 per minute. It brings the heartbeat to a normal level.
(a) Give any four reasons for Mendel’s success.
(b) Briefly describe the technique employed in DNA fingerprinting.
(c) Give any two features of Genetic Code.
(a) Four reasons for Mendel's success:
1. Pea plant was easy to grow and interbreed and had a short life cycle so that several generations could be produced within a short period.
2 The flowers are bisexual containing both male and female parts. They are self-fertilising in nature. Because of easy self-fertilization, it is easy to get pure lines for several generations.
3. The pea plants had a number of contrasting characters.
4. It was easy to hybridise because pollen from one plant could be introduced into the stigma of another plant by removing anthers.
(b) DNA fingerprinting involves a number of important steps in order to fully complete and develop and DNA fingerprint.
1. The process of DNA fingerprinting starts with isolating DNA from any part of the body such as blood, hair roots, teeth, bones, etc.
2. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the next step in the process. In many situations, there is only a small amount of DNA available for DNA fingerprinting. PCR is used to amplify the small amount of DNA. It involves three steps Denaturation, annealing and extension.
3. After the DNA is isolated and more copies of the DNA have been made, the DNA wis treated with restriction enzymes (an enzymes that cuts DNA near specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites). This is done to produce different sized fragments which are known as restriction fragment length polymorphisms.
4. These fragments can then be observed doing an experiment called gel electrophoresis which separates DNA based on fragment sizes.
Gel electrophoresis is the next step in this process of DNA fingerprinting. During gel electrophoresis, an electrical current is applied to a gel mixture, which includes the samples of the DNA. The electric current causes the DNA strands to move through the gel. This separates the molecules of different sizes. The fragments of separated DNA are sieved out of the gel using a nylon membrane (treated with chemicals that allow for it to break the hydrogen bonds of DNA so there are sing strands). The DNA (single stranded) is cross-linked against the nylon using heat or a UV light. The probe shows up on photographic film because the strands of DNA decay and give off light. In the end, it leaves dark spots on the film which are also known as the DNA bands of a person. What makes up the fingerprint are the unique patterns of bands. The pattern of bands are different because we are all different and unique (other than identical twins).
5. Once the filter is exposed to the x-ray film, the radioactive DNA sequences are shown and can be seen with the naked eye. This creates a banding pattern or what we know as DNA fingerprints. This technique is called southern blotting.
(c) Two features of the genetic code.
i. It is triplet and universal. The genetic code is called a universal code because all known organisms use the same four nucleotide bases; organism differ according to the arrangement of the nucleotide bases. The four nucleotide bases are adenosine, thymidine, cytidine and guanosine.
ii. Degenerative -The genetic code is degenerate because there are many instances in which different codons specify the same amino acid.
Each of the following question(s)/statement(s) has four suggested answers. Choose the correct option in each case.
The genotype of a person with Turner’s syndrome will be:
44+XXY
44+XYY
44+XO
44+XO
C.
44+XO
