For a metallic conductor, what is the relation between current density (J), conductivity ( ) and electric field Intensity (E)?
) and electric field Intensity (E)?
The relation between current density (J), conductivity ( ), and electric field intensity (E) is,
), and electric field intensity (E) is,
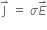
D.
A high resistance in parallel with its coil.Chose the correct alternative A, B, C or D
In current electricity. Ohm’s law is obeyed by all:
solids
metals
liquids
gases
B.
metals
The current flowing through a conductor is given by I = neAvd.
(i) Identify each term in the equation.
(ii) Obtain an expression for vd, if the current flowing through the conductor of length I has its ends maintained at a potential difference of V volts.
i) In expression
I = n e AVd
where
I = Current flowing through the conductor
n = Number of free electrons
e = Charge on the electron
A = Area of cross-section
Vd = Drift velocity.
(ii) Let e is the electronic charge and
m = Mass of each electron.
V = Potential difference across the conductor
I = Length of conductor
Then,
E = ![]() ... (i)
... (i) 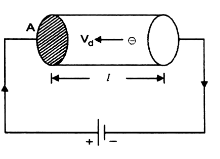
Hence, under the influence of electric field E electron experience a force given by,
F = qE
Acceleration of each electron is,
a = e E / m ... (ii)
At any instant of time, the velocity of an electron having thermal velocity u1 will be ![]() where
where ![]() of the time that has elapsed since its last collision.
of the time that has elapsed since its last collision.
So, for n electron, 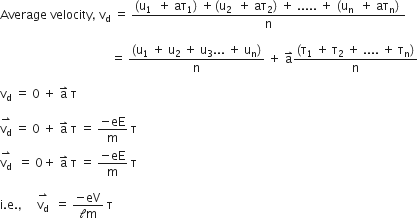
where, ![]() is the relaxation time.
is the relaxation time.
A carbon resistor has coloured bands as shown in fig. 2 below. The resistance of the resistor is:
26 
 10%
10%
26 
 5%
5%
260 
 5%
5%
260 
 10%
10%
C.
260 
 5%
5%
