
Write formulas for the following compounds:
(a) Mercury (II) chloride
(b) Nickel (II) sulphate
(c) Tin (IV) oxide
(d) Thallium (I) sulphate
(e) Iron (III) sulphate
(f) Chromium (III) oxide
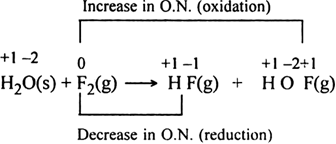
Consider the reactions:
Why is it more appropriate to write these reactions as:
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the above (a) and (b) redox reactions.
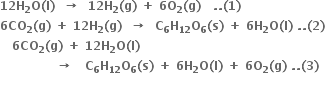
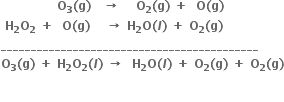
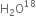 in reaction (a) or by using
in reaction (a) or by using 

In hydrogen peroxide H2O2, the oxidation number of O is -1 and the range of the Oxidation number that O can have are from O to -2 can sometimes also attain the oxidation numbers +1 and +2. Hence, H2O2 can act as an oxidising as well as reducing agent.


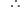 Oxidation number of P in NaH2PO4 = 5
Oxidation number of P in NaH2PO4 = 5
