(i) NF3 is an exothermic compound whereas NCl3 is not.
(ii) F2 is most reactive of all the four common halogens.
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) C + H2SO4 (conc.)-->
(ii) P4 + NaOH + H2O-->
(iii) Cl2+F2 ------>
(excess)
(i) As we move down the group 17, the size of the atom increases from fluorine to chlorine. The larger difference in the size of N and Cl results in the weakness of strength of N-Cl bond.
On the other hand, the difference in size of N and F is small; consequently, the N-F bond is quite strong. As a result, NF3 is an exothermic compound.
(ii)
1. F-F bond has low enthalpy because the fluorine atom has a small size and due to their small size, there is repulsion between two atoms making its bond enthalpy lower, hence more reactivity is more.
2. It has a small size and high charge density due to which it is the most electronegative element.
(a) Account for the following:
(i) The acidic strength decreases in the order HCl > H2S > PH3
(ii) Tendency to form pentahalides decreases down the group in group 15 of the periodic table.
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) P4 + SO2Cl2-->
(ii) XeF2 + H2O--->
(iii) I2+HNO3(conc.)--->
(i) The acidity of a molecule depends on the polarity of the bond between central atom and the hydrogen atom. Greater the polarity higher will be the acidity.
And the polarity of the bond depends on the electronegativity of the central atom. In a period, the electronegativity decreases in the order Cl > S > P. As a result, the loss of H+ ions decreases.
Thus, the acidic strength of the hydrides decreases in the
Following order:
HCl > H2S > PH3
(ii) Nitrogen does not form pentahalide because it does not have d-orbital. P, As, Sb form pentahalide. Bi does not form pentahalide. The tendency to form pentahalide decrease down the group. This because of inert pair effect.
Due to the inert pair effect, ns2 electron remains inert in a chemical reaction and element shows -2 oxidation state. Inert pair effect increases down the group. Thus the tendency to form pentahalides decrease down the group 15.
(b)
(i) P4 + 10SO2Cl2---> 4PCl5 + 10SO2
(ii) 2XeF2 + 2H2O----> 2Xe + 4HF + O2
(iii) I2 + 10HNO3--> 2HIO3+10NO2+4H2O
The reaction of zinc with dilute and concentrated nitric acid, respectively, produces:
NO2 and NO
NO and N2O
NO2 and N2O
NO2 and N2O
D.
NO2 and N2O
Zn + 4 HNO3 (conc.)→ Zn(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
4Zn + 10HNO3 (dil) → 4Zn(NO3)2 + N2O + 5H2O
(a) Draw the molecular structure of the following compounds.
(i) N2O5
(ii) XeOF4
(b) Explain the following observation:
(i) Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.
(ii) ICI is more reactive than I2.
(iii) Despite the lower value of its electron gain enthalpy with a negative sign, fluorine (F2) is a stronger oxidizing agent than Cl2.
i) 
ii)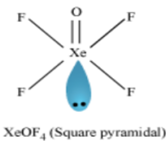
(b)
(i) Due to the small size of oxygen, it has less tendency for catenation and the high tendency of pp-pp multiple bonds, hence forms stable O2 molecules whereas sulphur because of its higher tendency for catenation and lesser tendency to form pp-pp multiple bonds forms S8 molecules having 8-membered puckered ring.
(ii)Inter -halogen bonds are weaker (it is between two different halogen like ICl) because of its partly ionic character due to the difference in electronegativity.
While when the same halogen forms X2 molecules like I2. They form covalent bonds which are stronger than interhalogen compound and weak bond obviously is more reactive than the stronger bond and that’s why ICl is more reactive than I2.
(iii) Fluorine is a much stronger oxidising agent than chlorine. The oxidising power depends on three factors.
1. Bond dissociation energy
2. Electron gains enthalpy
3. Hydration enthalpy
The electron gain enthalpy of chlorine is more negative than that of fluorine.
However, the bond dissociation energy of fluorine is much lesser than that of chlorine. Also, because of its small size, the hydration energy of fluorine is much higher than that of chlorine. Therefore, the latter two factors more than compensate for the less negative electron gain enthalpy of fluorine. Thus, fluorine is a much stronger oxidising agent than chlorine.
(i) Which allotrope of phosphorus is more reactive and why?
(ii) How the supersonic jet aeroplanes are responsible for the depletion of ozone layers?
(iii) F2 has lower bond dissociation enthalpy than Cl2. Why?
(iv) Which noble gas is used in filling balloons for meteorological observations?
(v) Complete the equation: XeF2 + PF5 →
i) White phosphorus is most reactive of all the allotropes of phosphorus because it is unstable due to the angular strain on P4 molecule with the bond angle of 60°.
(ii) Nitrogen oxide emitted from the exhausts of supersonic jet aeroplanes readily combine with ozone to form nitrogen dioxide and diatomic oxygen.
NO(g) + O3(g) →NO2(g) +O2(g)
Since supersonic jets fly in the stratosphere near the ozone layer, they are responsible for the depletion of ozone layer.
(iii) The size of a fluorine atom is very small as compared to a chlorine atom. Therefore, the repulsion between electrons in the outer most shell of the two atoms in a fluorine molecule is much greater than that in a chlorine molecule. Hence, it requires less energy to break up the fluorine molecule, making its bond dissociation energy lesser than that of chlorine molecule.
(iv) Helium, being light, non-inflammable and unreactive, is used for filling of balloons for metrological observations.
(v) XeF2 + PF5→ [XF]++[PF6]-
