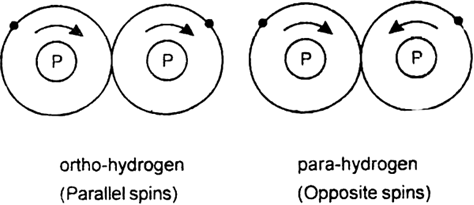
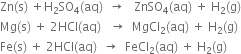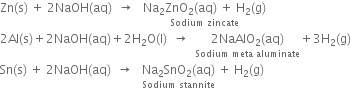What are isotopes? Discuss briefly the various isotopes of hydrogen.
Isotopes: Isotopes are the atoms of the same element having the same number of electrons and protons but a different number of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mas-numbers.
Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties because of the presence of an equal number of electrons in their extra nuclear parts. Chemical properties of an element are dependent only on the number of electrons and their distribution in various shells around the nucleus. Isotopes of the same element differ in their physical properties because these isotopes differ in the number of neutrons which cause a difference in the mass numbers.
Isotopes of hydrogen:
Three isotopes of hydrogen are known. They are:
(i) Protium or ordinary hydrogen or light hydrogen  It is the most abundant isotope of hydrogen. Its atomic number is 1 and mass number is 1. Its nucleus consists of one proton and has one electron in the 1s orbital. It is a non-radioactive isotope of hydrogen.
It is the most abundant isotope of hydrogen. Its atomic number is 1 and mass number is 1. Its nucleus consists of one proton and has one electron in the 1s orbital. It is a non-radioactive isotope of hydrogen.
(ii) Deuterium or heavy hydrogen 
It is present in heavy water (D2O) and can be recovered from it by fractional electrolysis. Its atomic number is 1 and mass number is 2. Its nucleus consists of one proton and one neutron and has one electron in the 1s orbital. It is a non-radioactive isotope of hydrogen.
(iii) Tritium  Its atomic number is 1 and mass number is 3. Its nucleus consists of one proton and two neutrons and has one electron in the 1s orbital. Tritium is the only radioactive isotope of hydrogen.
Its atomic number is 1 and mass number is 3. Its nucleus consists of one proton and two neutrons and has one electron in the 1s orbital. Tritium is the only radioactive isotope of hydrogen.

The electronic configuration of all the isotopes of hydrogen is same, therefore, chemical properties of all the isotopes are identical. However, they differ from each other in their rates of reaction and equilibrium constants for reversible reactions e.g. protium reacts with chlorine 13.4 times as fast as deuterium does.
Due to the difference in the masses of the isotopes of hydrogen, they have different physical properties. Property differences arising from differences in mass are called isotopic effects.
Properties: The difference in the masses of protium and deuterium produce appreciable changes in many of their physical properties like melting point and boiling point, latent heat of fusion, evaporation, sublimation etc. As deuterium is heavier than hydrogen, so the rates of a reaction involving deuterium are slower than reactions involving hydrogen. For the same reason, D2 has a higher boiling point than that of H2.
Write a short note on allotropy of hydrogen.
Or
How many allotropes of dihydrogen are known? What is their importance?
How would you prepare dihydrogen from water using a reducing agent?
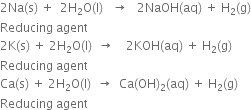
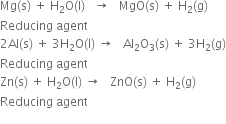
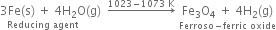

How would you prepare dihydrogen from a substance other than water?