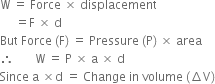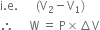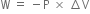Give the points of difference between reversible process and irreversible process.
|
Reversible process |
Irreversible process |
|
1. Such processes take place infinitesimally slowly and their direction at any point can be reversed. |
1. The process cannot be reversed. |
|
2. It is a slow process. |
2. It is a fast process. |
|
3. This process is in equilibrium at all stages of operation. |
3. There is no equilibrium. |
|
4. This is an ideal and imaginary process. |
4. It is a real process. |
What do you mean by internal energy and internal energy change?
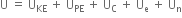
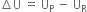


 the extra energy possessed by the system in the initial state (or the reactants) would be given out and
the extra energy possessed by the system in the initial state (or the reactants) would be given out and  will be negative.
will be negative.  energy will be absorbed in the process and
energy will be absorbed in the process and  will be positive.
will be positive.Derive an expression for work done in isothermal reversible expansion of ideal gas.
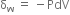
 Total work done when the gas expands from initial volume V1 to final volume V2, will be
Total work done when the gas expands from initial volume V1 to final volume V2, will be
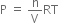
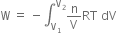
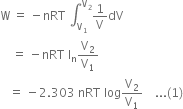
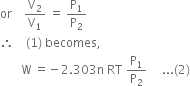
What do you understand by:
(i) Isothermal process
(ii) Adiabatic process
(iii) Isobaric process
(iv) Isochoric process
(v) Cyclic process?
(i) Isothermal process: A process is said to be isothermal if the temperature of the system remains constant i.e. operation is carried at a constant temperature. For an isothermal process, dT = 0 where dT is the change in temperature.
(ii) Adiabatic process: In an adiabatic process, no heat can flow from the system to the surrounding or vice versa i.e. the system is completely insulated from the surroundings.
(iii) Isobaric process: It is the process during which the pressure of the system is kept constant i.e. dP = 0. The volume may or may not change.
(iv) Isochoric process: It is a process during which the volume of the system is kept constant i.e dV = 0.
(v) Cyclic process. When a system undergoes a series of changes and finally returns to its initial state, it is an example of the cyclic process. In cyclic process dU = 0.