 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAssume a new sub‐species Ficus callosa subsp microcarpa has been published by Jacobs. The nomenclature of the resulting entities would be
F callosa and F. callosa subsp. Microcarpa Jacobs
F. callosa subsp. Mocrocarpa Jacobs and other yet to be named subspecies of F. callosa
F. callosa subsp. Callosa Jacobs and F. callosa subsp. Microcarpa Jacobs
F. callosa subsp. Callosa and F. callosa subsp. Microcarpa Jacobs
D.
F. callosa subsp. Callosa and F. callosa subsp. Microcarpa Jacobs
The nomenclature of the resulting entities would be F. callosa subsp. Callosa and F. callosa subsp. Microcarpa Jacobs.
Primary production in aquatic ecosystem is measured using Light and Dark bottle technique. In this method, as an indirect measure of photosynthetic production, dissolved oxygen concentration of the pond water enclosed in a BOD bottle is measured initially (I) and after a fixed duration of incubation in a light bottle (L) and a dark bottle (D). Then the gross and net primaty pdocuctions are estimated is
(L‐D) and (L‐I), respectively
(L‐I) and (L‐D) respectively
(L‐I) and (I‐D) respectively
(L‐D) and (I‐D) respectively
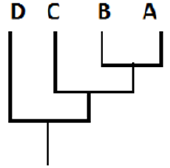
Identify the most appropriate cladogram that can be constructed using the data matrix given below, assuming ‘o’s are pleisomorphic and ‘1’ are apomorphic characters
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| A | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| C | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| D | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |



Gause’s competitive exclusion principle states that two species with identical niches cannot coexist indefinitely. Which of the following statements is the most appropriate regarding the validity of the principle?
It depends on how one defines niche
There are in nature many instances of continued coexistence of closely related species
The principle is universally true
It does not predict the outcome where, both the species are equally strong competitors
In a lake ecosystem, bottom up effects (B) refers to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels – Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and Carnivore (C),
P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T
P, Z and C are all controlled by T
P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B
P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T
An organism has the following architectural pattern:
(i). Multicellular with germ layers
(ii). A coelom derived from the mesoderm
(iii) Primary bilateral symmetry with secondary radial symmetry
(iv) Presence of endo‐skeletal plates
Such an organism is most likely to
A. Have mesohymal as its connective tissue
B. Undergo torsion, whereby the mouth and anus are properly oriented
C. Be devoid of a brain but have calcareous spicules
D. Have comb plates to help in locomotion
Which of the following is true?
A and C
C only
D only
B and C
Identify the apomorphic characters marked in the cladogram:
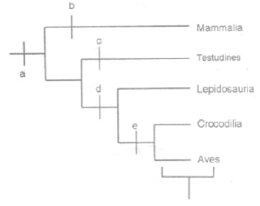
A‐ amniotic egg; b‐ 4 chambered heart; c‐anapsidian skull; d‐diapsidian skull; e‐synapsid skull
A‐amniotic egg; b‐synapsidian skull; c‐4 chambered heart; d‐anapsidan skull; e‐diapsidan skull
A‐4 chambered heart; b‐synapsid skull; c‐aminiotic egg; d‐diapsidan skull; eanapsidan skull
A‐amniotic egg; b‐synapsidan skull; c‐anapsidan skull, d‐diapsidan skull; e‐4chambered heart.
The graph below shows the relationships of per capita population growth rate (r), fecundity (b) and age at first reproduction (α) in an animal species What is the most important conclusion to be drawn from the graph?
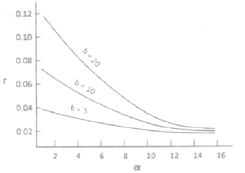
The later the age of first reproduction, the lower is the population growth rate achieved
The population growth rate decreases as first reproduction is postponed to a later stage, regardless of the fecundity
At any α, the higher the fecundity, the higher is the population growth rate achieved
As the age at first reproduction is postponed further, the benefits of increasing fecundity on the population growth rate become progressively negligible.
What will be the approximate effective population size in a panmictic population of 240 with 200 females and 40 polygamous males?
160
133
63
67
An animal was first maintained in a constant environmental condition for several days until a consistent biological rhythm (B) was established. The animal as then exposed to an experimental physical rhythm (E) which modulate the phase and period of B. However, upon withdrawal of E, the B gradually regained its pattern of pre‐exposure condition. Form these observations which one or more of the following should be the most logical interference?
A. E is a zietgeber
B. E is a masking agent
C. E cause entrainment of B
D. B is conditioned to E
The correct answer is
A and C
B and D
B only
D only
