 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn an experiment on transposition in an eukaryotic system, an intron was cloned within a transosable element and allowed to transpose from a plasmid to genomic DNA. The intron was found to be absent in the transposable element in its new location. It is
not a case of transposition.
a case of replicative mode of transposition.
a case of conservative mode of transposition.
a retrotransposon
D.
a retrotransposon
The intron was found to be absent in the transposable element in its new location because it is a retrotransposon.
In a plant species, a segregating line (one that contains both homozygotes and heterozygotes at a locus) can be made homozygous by repeated selfing for several generations. What is the level of remaining heterozygosity after three generations of selfing, if the level of heterozygosity in generation'0' is denoted as 1?
0.5
0.25
0.125
0.0625
Given below is the result of a complementation test for six independent mutants(1 to 6).
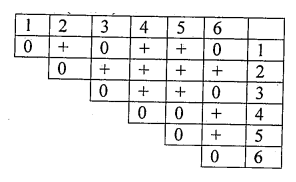
'+' represents complementation; '0' represents non-complementation.
Based on the above, which one of the following conclusions is correct?
The mutations can be ordered in a single cistron as 1-3-5-2-4-6.
All mutations belong to a single cistron, but their order cannot be determined.
There are three cistrons, mutations 1, 3, and 6 represent one cistron, 4 and 5 represent the second cistron and 2 represents the third cistron.
There are three linkage groups, mutations 1, 3 and 6 represent linkage group A, 4, and 5 represent linkage group B, and 6 represents linkage group C.
In a hospital three babies were mixed up. the blood group of the babies were A, B and AB. In order to identify the parents of the babies the blood groups of the parents were determined. the results obtained were:
Parent set 1 - A and AB
Parent set 2 - AB and O
Parent set 3 - B and AB
Which of the following conclusions can be definitively made?
The baby with blood group A is the child of the parent set 2.
The baby with blood group AB is the child of the parent set 1.
The baby with blood group B is the child of the parent set 3.
The parentage of none of the babies can be determined from the given information.
There are two mutant plants. One shows taller phenotype than wild type, whereas the other has the same height as the wild type. When these two mutations were brought in together by genetic crosses, the double mutant displayed even taller phenotype than the tall mutant plants. This genetic interaction is called
antagonistic interaction
additive interaction
synergistic interaction
suppressive interaction
The following table gives vascular tissue characteristics of four divisions of Tracheophyta.
| Divisions | Vascular tissue characteristics |
| A. Psilophyta | i. Well-developed tracheid and pits in lateral wall |
| B. Lycopodiophyta | ii. Tracheids |
| C. Sphenophyta | iii. Tracheids, vessels and well-developed phloem |
| D. Pteridophyta | iv. Primitive tracheids and pits in lateral wall |
Identify the correct combinations.
A - i; B- ii; C - iii; D - iv
A - ii; B - i; C - iv; D - iii
A - iv; B - iii; C - ii; D - i
A - iii; B - iv; C - i; D - ii
Which of the following is NOT an advantage to seed-based reproduction?
Reserve food material is provided for the developing embryo.
Seed coat protects the embryo and allows it to remain dormant until favourable environmental conditions are available.
The amount of energy spent per female gametophyte is less than that spent on making a spore.
The female gametophyte remains on the sporophyte which provides protection and nourishment.
In a study of sexual isolation in a species of salamander, scientists brought together males and females from different populations and from the same population. they observed the frequency of mating and calculated a sexual isolation index. One graph shows the relationship between mating frequency and genetic distance, and the other shows the relationship between sexual isolation index and geographic isolation.
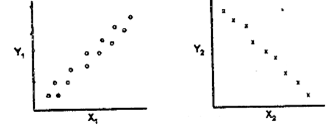
Choose the appropriate terms for X1, Y1, X2, and Y2 in the figures above
X1= geographic distance; Y1 = sexual isolation index; X2 = gentic distance; Y2 = mating frequency
X1= geographic distance; Y1 = mating frequency; X2 = gentic distance; Y2 = sexual isolation index
X1= gentic distance; Y1 = mating frequency; X2 = sexual isolation index; Y2 = geographic distance
X1= gentic distance; Y1 = geographic distance; X2 = sexual isolation index; Y2 = mating distance
As per the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature, 2006 (Vienna Code), which of the following is a Nothospecies?
Polypodium vulgare subsp. prionodes (Asch.) Roth.
Polypagon monspeliensis (L). Desf.
Agrostis stolonifera L.
Agrostis stolonifera L. × Polypogon monspeliensis (L.) Desf.
Which of the following groups have only two wings?
Honey bee, beetle, ant
Butterfly, housefly, fruitfly
Dragonfly, butterfly, fruitfly
Housefly, fruitfly, mosquito
