 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA gene is regulated by a novel transcription factor. the following techniques may be used to identify the cis-regulatory element in the 1 kb promoter sequence of the gene where the novel transcription factor binds:
A. Bioinformatics analysis.
B. Cell based reporter assay.
C. S1 nuclease assay.
D. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
E. DNAse-1 foot-printing analysis
Which one of the following can help to identify the cis element?
A and B
C and E
D only
E only
D.
E only
The statement that can help to identify the cis-element is statement E.
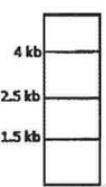
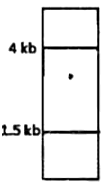
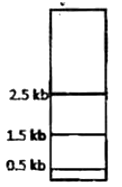
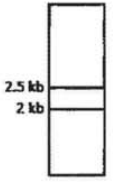
A protein D is encoded by a gene, which is 5 Kb long and has three Hind III restriction enzyme sites. The first one is 0.5 Kb from the transcription start site, the second one if 2.5 Kb from the first site and the third one is 0.5 Kb internal to the stop codon. The second site is polymorphic. In order to find out whether fetal cells contain the normal or the mutated gene, total genomic DNA from fetal cells was isolated, completely digested with Hind III, separated in an agarose gel, transferred to membrane and detected by a probe against the region between the second and third restriction site. Which one of the following band patterns will be obtained if the fetal cell is heterozygous?
Given below are the experimental protocols to find out the exact location of repetitive DNA sequence in mitotic chromosome by FISH (Fluorescence in situ hybridization). Which one of the protocols will give the correct result?
Mitotic chromosomes were fixed on glass slide → incubated with biotinylated telomeric DNA → denatured → incubated with fluorescently labeled avidin → localization observed under a fluorescence microscope.
Mitotic chromosomes were fixed on glass slide → denatured → incubated with FITC labeled unrelated non-repetitive DNA sequence → counterstained with propidium iodide → localization observed under fluorescence microscope.a
Mitotic chromosomes were fixed on glass slide → denatured → incubated with biotinylated satellite DNA → incubated with fluorescently labeled avidin → localization observed under fluorescence microscope
Mitotic chromosomes were fixed on glass slide → incubated with repetitive DNA sequence binding protein → denatured → FITC labeled antibody against the protein → localization observed under fluorescence microscope.
At 25°C values of [θ]222, the mean residue ellipticity at 222nm, are -33,000 and -3,000 deg cm2 dmol-1 for a polypeptide existing in α-helical (α) and β-structure (β), respectively. If this polypeptide undergoes a two-state heat induced α → β transition, and a value of [θ]222 = -18,000 deg cm2 dmol-1 is observed at 60°C, then this observation leads to the conclusion that the α -helix conversion to β-structure is:
40%
50%
55%
60%
An EEG was recorded and its power spectrum analyses were done in rats with implanted electrode for a long time. The power of the EEG waves decreased two months after electrode implanation.
This observation may be due to the following:
A. Glial cells accumulate surrounding the exposed tips of electrodes.
B. Degeneration of neurons occur surrounding the electrode tips due to metal ion deposition.
C. Coating of electrodes are destroyed with time.
D. The microsocket becomes loose with time.
Which one of the following is true?
Only A
A and B
Only C
C and D
