 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsMarker-assisted selection (MAS) defined as selection based on molecular markers should have some important criterion for plant breeding activities. Some statements about these criteria are mentioned below:
A. Marker should co-segregate with the desired trait of interest.
B. Marker should not co-segregate with the desired trait of interest.
C. Marker should be un-linked with the desired trait of interest.
D. Marker is used for indirect selection of a genetic determinant or determinants of a trait of interest.
Which one of above combinations is correct?
A and B
B and C
C and D
A and D
C.
C and D
Among the given options, the correct combination is of statements C and D.
In a transgenic mice line, lox P sites are introduced in the target gene A in the following manner
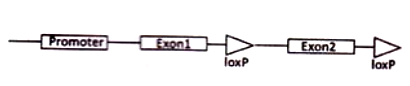
This transgenic mice line was mated with another transgenic mice line where Cre recombinase is expressed only in B cells. What will be the expression profile of gene A in Cre/lox recombinant mice?
Gene will not be expressed in B cells, as the orientation of exon 1 will be inverted by Cre.
Gene will not be expressed in B cells, as exon 2 will be deleted by Cre.
Gene will only be expressed in B cells of the recombinant mice where Cre removes the two lox P sites.
Gene will not be expressed in B cells as orientation of exon 2 will be inverted.
A hypothetical gene encodes a protein with the following amino acid sequence:
Phe-Pro-Thr-Ala-Val-Arg-Ser
A mutation of single nucelotide alters the amino acid sequence to
Phe-Leu-Leu-leu-Leu-Val
A second single nucleotide mutation occurs in same gene restoring back the amino acid sequence to the original.
The following statements were made regarding the nature and location of the first mutation and that of the intragenic suppressor mutation:
A. The first mutation is a deletion in the second codon.
B. the first mutation is an insertion in the second codon.
C. The intragenic suppressor mutation is an insertion in the second codon.
D. The intragenic suppressor mutation is a deletion in the third codon.
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
A and C
A and D
B and C
B and D
Three Indian animals- cormorant, lion-tailed macaque and gerbil are to be matched with the ecosystem they inhabit-Wetland (A), Deser (B), Deciduous forest (C), or Rain forest (D). Which of the following is the correct match of each animal with its habitat?
Cormorant - D; Lion-tailed macaque - C; Gerbil - B
Cormorant - A; Lion-tailed macaque - C; Gerbil - D
Cormorant - A; Lion-tailed macaque - D; Gerbil - B
Cormorant - B; Lion-tailed macaque - C; Gerbil - D
The following table summarizes the result of a cross between two strains of Neurospora having the alleles D and d, respectively. The table shows the different patterns of octad arrangement and the number of ascus observed if each type.
| D | d | D | d | D | d |
| D | d | D | d | D | d |
| D | d | d | D | d | D |
| D | d | d | D | d | D |
| d | D | D | d | d | D |
| d | D | D | d | d | D |
| d | D | d | D | D | d |
| d | D | d | D | D | d |
| 115 | 125 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 13 |
Number of ascus observed = 300
Based on the above, fill in the blanks from the options given below:
"The first two columns are from meiosis with no crossover between locus D and [A]. The patters for these two columns represent [B] segregation pattern. the distance between the locus D and the centromere is [C] map units."
[A] - d allele; [B] - first division; [C] - 10
[A] - centromere; [B] first division; [C] 10
[A] d allele; [B] - second division; [C] - 20
[A] - centromere; [B] - second division; [C] - 10
The inheritance pattern of a common trait which shows complete penetrance is shown below:
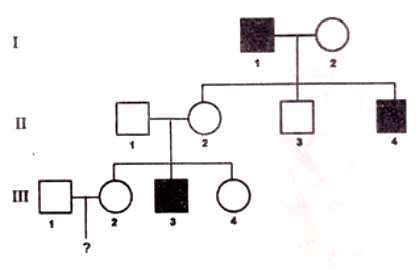
Based on the above pedigree, fill in the blanks from the options given below:
"The trait is [A[. The probability that a child from the marriage of individual III-1 and III-2 will show the trait is [B], considering that the individual III-1 is a carrier of the trait."
[A] - Y-linked; [B] - 0
[A] - Y-linked; [B] - 1/2
[A] - Autosomal; [B] - 1/8
[A] - Autosomal; [B] - 1/6
The following statements were made regarding chromosome pairing (shown in the figure below) and subsequent segregation during meiosis - I in the reciprocal translocation heterozygote:
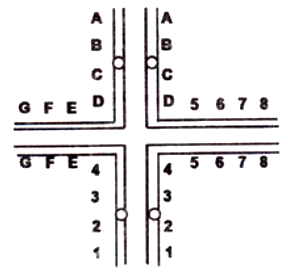
A. Three ways of segregation in Anaphase I would be : adjacent 1 (vertically in the above figure), adjacent 2 (horizontally and alternate.
B. Gametes resulting from adjacent 1 and adjacent 2 segregation will be non-viable because of deletions and duplications of several genes.
C. All gametes resulting from alternate segregation will be viable as they will carry both normal chromosomes or both chromosomes having translocations in the two plea, respectively.
D. A dicentric and acentric chromosome will be generated following alternate segregation.
Which of the following combination of statements will most appropriately explain the consequence?
A, B and D
A, B and C
Only A and B
Only A and C
The list below includes names of animal phyla and classes.
A. Echinodermata
B. Cephalopoda
C. Annelida
D. Mollusca
E. Hirudinea
F. Asteroidea
G. Arthropoda
H. Crustacea
For a leech and lobster, the correct classification of phylum and class respectively, is
Leech: Phylum-D, Class-B;
Lobster: Phylum-A, Class-H
Leech: Phylum-C, Class-B;
Lobster: Phylum-D, Class-C
Leech: Phylum-C, Class-E;
Lobster: Phylum-G, Class-H
Leech: Phylum-A, Class-G;
Lobster: Phylum-C, Class-F
10mM acetate buffer (pH 4.00) is diluted one million times with distilled water (pH 7.00). pH of this diluted buffer is:
4.00
7.04
8.00
6.96
Consider the structureless oligopeptide, R-G-P-S-T-K-M-P-E-Y-G-S-T-D-Q-S-N-W-H-F-R. The number of bonds that will be cleaved by trypsin and chymotrypsin treatments separately, are:
1, 2
2, 2
2, 3
1, 3
