Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo kinds of natural selection (A and B) acting on a trait are shown in the figure below. In each, the top graph shows the trait frequency before and the bottom graph frequency after the action of natural selection.
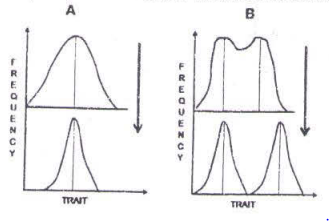
The kind of natural selection in A and B are
A - Directional; B- Diruptive
A - Neutral; B - Disruptive
A - Stabilizing; B - Disruptive
A - Disruptive; B - Stabilizing
C.
A - Stabilizing; B - Disruptive
The kind of natural selection in A and B are Stabilizing and Disruptive, respectively.
In a random sample of 400 individuals from a population with alleles of a trait in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 36 individuals are homozygous for allele a. How many individuals in the sample are expected to carry at least one allele A?
36
168
364
196
Individual A performs to another individual a behavioural act which has a fitness consequence. Match the behavioural acts (a to e) with the correct fitness consequence ((i) to (iv)).
| Behavioural act | Fitness consequence to A |
| Cooperation (a) | Gains direct fitness but after delay (i) |
| Adaptive altruism (b) | Loses inclusive fitness (ii) |
| Spite (c) | Gain indirect fitness (iii) |
| Deceit and manipulation (d) | Gains direct fitness but immediately (iv) |
| Reciprocity (e) |
a - (iv); b - (iii); c - (ii); d - (ii); e - (i)
a - (i); b - (ii); c - (ii); d - (iii); e - (iv)
a - (i); b - (iii); c - (ii); d - (ii); e - (iv)
a - (ii); b - (ii); c - (iii); d - (i); e - (iv)
Assume that individual A wants to do an altruistic act to individual B and that the benefit and cost of doing this act are, in 'fitness' units, 40 and 12, respectively. According to Hamilton's Rule, A should perform the altruistic act only if B is his
nephew
niece
grandson or granddaughter
daughter or son
Which of the following is NOT a benefit for the female adopting polyandry?
Greater probability of getting all her eggs fertilized.
Ability to receive more resources from the males.
Ability to produce more offspring than normal.
Improved chances of genetic compatibility with her own DNA.
Which of the following is the correct decreasing order for the rate of decomposition of litter constituents?
Hemicellulose, cellulose, lignin, phenol
Cellulose, hemicellulose, phenol, lignin
Hemicellulose, cellulose, phenol, lignin
Lignin, phenol, hemicellulose, cellulose
Complete the following hypothetical life of a species to calculate the net reproductive rate R0:
| Age class (x) | Number alive (nx) | Number of dying (dx) | Age-specific survivorship | Age-specific Fertility | lxmx |
| 0-1 | 1000 | 0 | |||
| 1-2 | 800 | 0 | |||
| 2-3 | 200 | 0.5 | |||
| 3-4 | 300 | 100 | 1.0 | ||
| 4-5 | 200 | 1.0 |
The calculated R0 will be:
0.75
1.00
0.65
1.15
Following four types of species were observed in a community:
A. Species A has a large effect on community because of its abundance.
B. Species B has a large role in community out of proportion to its abundance.
C. Status of species C provides information on the overall health of an ecosystem.
D. Significant conservation resources are allocated to species D which is single, large and instantly recognizable.
According to above description, species A, B, C, and D are called respectively,
Dominant, Keystone, Indicator and Flagship
Keystone, Flagship, Dominant and Indicator.
Keystone, Dominant, Indicator and Flagship.
Flagship, Dominant, Keystone and Indicator
The diagram represents the competition between species 1 and species 2 according to Lotka-Volterra model of competition.
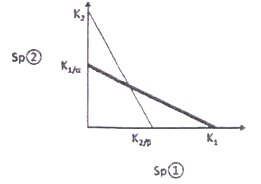
Given the conditions in the diagram, the predicted outcome of competition is
Unstable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 > K2/β and K2 > K1/α.
Unstable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 < K2/β and K2 < K1/α.
Stable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 > K2/β and K2 > K1/α.
Stable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 < K2/β and K2 < K1/α.
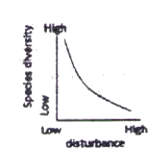
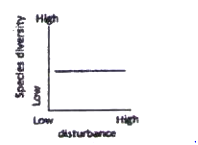
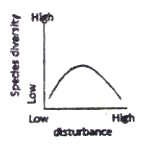
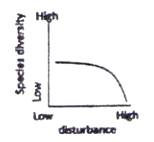
The possible relationships between level of disturbance and species diversity in a biological community are that species diversity.
A. is unaffected by disturbance.
B. is highest at intermediate levels of disturbance.
C. decreases exponentially with increasing levels of disturbance.
D. starts decreasing only at higher levels of disturbance.