 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn a population of effective population size Ne, with rate of neutral mutation μ0, the frequency of heterozygotes per nucleotide site at equilibrium between mutation and genetic drift is calculated as
B.
In a population of effective population size Ne, with rate of neutral mutation μ0, the frequency of heterozygotes per nucleotide site at equilibrium between mutation and genetic drift is calculated as-
The "Red Queen Hypothesis" is related to
the mating order in the harem of a polygamous male.
the elimination by deleterious mutations by sexual reproductions.
mate selection process by a female in a lek.
the evolutionary arms race between the host and the parasite.
Individual A can derive 'fitness' benefit of 160 units by helping Individual B, but incurs a 'fitness' cost of 50 units in doing so. Following Hamilton's Rule, A should help B ONLY if B is his
brother or sister
first cousin only
cousin or uncle
nephew or niece
In several populations, each of size N = 20, if genetic drift results in a change in the relative frequencies of alleles,
A. What is the rate of increase per generation in the proportion of populations in which the allele is lost or fixed?
B. What is the rate of decrease per generation in each allele frequency class between 0 and 1?
The correct answer for A and B is:
A - 0.25; B - 0.125
A - 0.025; B - 0.0125
A - 0.0125; B - 0.025
A - 0.125; B - 0.25
Following table shows the presence (+) or absence (-) of five species in three communities (A, B, C):
| Species | Community A | Community B | Community C |
| 1 | + | + | + |
| 2 | + | + | - |
| 3 | - | - | + |
| 4 | + | - | - |
| 5 | - | - | + |
Based on the above, which of the following is the correct order of similarity between two pairs of communities?
A and B > B and C > A and C
A and B > A and C > B and C
B and C > A and B > A and C
A and C > A and B > B and C
Following table shows the number of individuals of five tree species in a community:
| Tree species | No. of individuals |
| A | 50 |
| B | 20 |
| C | 20 |
| D | 05 |
| E | 05 |
Based on the above, the Simpson's diversity (DS) Index of the community will be
0.552
0.335
0.435
0.345
Which of the following X-Y relationships does NOT follow the pattern shown in the graph?
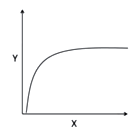
Number of prey killed (Y) in relation to prey density (X).
Photosynthetic rate (Y) in relation to light intensity (X).
Species richness (Y) in relation to area (X).
Tree species richness (Y) in relation to actual evapotranspiration.
In a field experiment, autotrophs are provided a 14C-labelled carbon compound for photosynthesis. Radioactivity (14C) levels were then monitored at regular intervals in all the trophic levels. In which ecosystem is the radioactivity likely to be detected fastest at the primary carnivore level?
Open ocean
Desert
Deciduous forest
Grassland
A population is growing logistically with a growth rate (r) of 0.15/week, in an environment with a carrying capacity of 400. What is the maximum growth rate (No. of individuals/ week) that this population can achieve?
15
30
22.5
60
Important chemical reactions involved in nutrient cycling in ecosystems are given below:
a. NO
b. N2 → NH3
c. NH
d. NO → N2
The organisms associated with these chemical reactions are
a - Nitrosomonas; b - Pseudomonas; c - Nostoc; d - Nitrobacter
a - Pseudomonas; b - Nitrobacter; c - Nostoc; d - Nitrosomonas
a - Nitrobacter; b - Nostoc; c - Nitrosomonas; d - Pseudomonas
a - Nostoc; b - Nitrosomonas; c - Nitrobacter; d - Pseudomonas
