 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsPolynucleotide kinase (PNK) is frequently used for radiolabeling DNA or RNA by phosphorylating 5'-end of non-phosohorylated polynucleotide chains. Which of the following statements about PNK is not true?
PNK catalyzes the transfer of α-phosphate from ATP to 5'-end of polynucleotide chains (DNA or RNA).
PNK has 3'-phosphatase activity.
PNK is inhibited by small amount of ammonium ions.
PNK is a T4-bacteriophage-encoded enzyme.
A.
PNK catalyzes the transfer of α-phosphate from ATP to 5'-end of polynucleotide chains (DNA or RNA).
PNK catalyzes the transfer of α-phosphate from ATP to 5'-end of polynucleotide chains (DNA or RNA) is an incorrect statement about PNK.
A gene encoding for protein X was cloned in an expression vector under the T7 RNA polymerase promoter and lac operator. Cells were induced by the addition of 1mM IPTG at 37°C for 6 h. Cells were lysed and fractionated into soluble bodies and cell-free supernatant by centrifugation. Protein X is present in the insoluble bodies. Which one of the following strategies would you use to express protein X in the soluble fraction (cell-free supernatant)?
Increase the duration of induction with 1mM IPTG.
Grow cells at lower temperatures after induction with 1mM IPTG.
Increase the concentration of IPTG.
Grow cells at higher temperature after induction with 1mM IPTG.
Engineering of metabolic pathways in plants can be achieved by introduction and overexpression of appropriate candidate gene(s) using transgenic technology. The figure given below represents a biochemical pathways in plants where a precursor molecule 'A' is converted into products 'T' and 'X' through a series of enzymatic reactions. Enzymes 1-5 are involved in this pathway. Scientists attempted to increase the level of 'X' by introducing an additional copy of the gene for enzyme '5' under transcriptional control of a strong constitutive promoter. However, the developed transgenic plants did not display a proportionate increase in the level of 'X'.
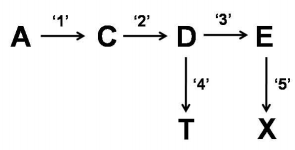
The following statements were proposed for explaining the above results:
A. Enzyme '4' has a greater affinity for D than enzyme '3'.
B. Feedback inhibition of enzyme '5' compound X.
C. Substrate limitation for enzyme '5'.
Which of the above statements could represent probable reasons for NOT obtaining a proportionate increase in the amount of X in the transgenic plants?
Only C
Only A and B
Only A
A, B, and C
A single copy homozygous transgenic plant containing the transgene A for fungal resistance was subsequently re-transformed with another gene 'B' for conferring resistance to salt-stress. The selection marker genes used for both the transformation experiments were different. Transgenic plants obtained following the re-transformation were screened for salt-stress resistance and single cop evens were identified by Southern hybridization. These single copy events were self-pollinated. In the event of the two T-DNAs (containing the A and B transgenes) getting integrated in unlinked locations in all the transgenic plants, the phenotypic ratios among the T1 progeny would be:
3 (Fungal resistant + Salt-stress resistant): 1 (Fungal resistant)
1 (fungal resistant) : 2 (Fungal resistant + salt stress resistant): 1(salt-stress resistant)
3 (Salt-stress resistant): 1(fugal resistant)
1(Fungal resistant): 1(Salt-stress resistant):1 (fungal resistant + salt stress resistant)
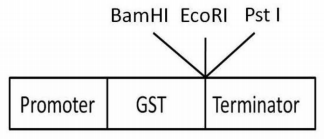
You are inserting a gene of 2kb length into a vector of 3Kb to make a GST fusion protein. Thegene is being inserted at the EcoRI site and the insert has a HindIII site 500bp downstream of the first codon. You are screening for the clone with the correct orientation by restriction digestion of the plasmid using HindIII plus BamHI (H+B) and HindIII plus PstI (H+P). The map of the relevant region of the vector is shown below:
Given below is the pattern following restriction digestion of plasmid isolated from four independent clones (A, B, C, and D).
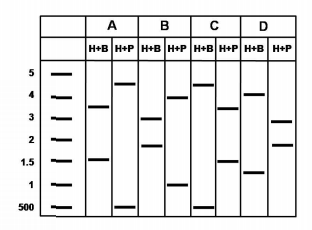
Which of the plasmids shown above represents the clone in the correct orientation?
A
B
C
D
