 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsChoose the most appropriate pH at which the net charge is zero for the molecule from the data shown below:
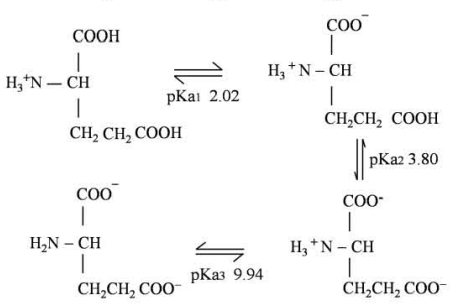
2.02
2.91
5.98
6.87
B.
2.91
At pH 2.91, the net charge will be zero for the molecule.
Choose the correct statement about peptides in the Ramachandran plot.
Peptides that are unstructured will have all the backbone dihedral angles in the disallowed regions.
It is not possible to conclude whether a peptide adopts an entirely helix or entirely beta-sheet conformation.
The occurrence of beta-turn conformation in a peptide can be deduced.
The sequence of a peptide can be deduced.
Equilibrium constant (K'eq) of a reaction is a ratio of product to substrate concentrations. The relation between (K'eq) and free energy change in a reaction (G') is as follows
Reaction A and Reaction B have K'eq values of 10 and 100, respectively. Which of the following statements is correct with respect to G'?
Excess oxygen consumed after a vigorous exercise is
to pump out lactic acid from muscle
to increase the concentration of lactic acid in muscle.
to reduce dissolved carbon dioxide in the blood.
to make ATP for gluconeogenesis
Which one of the following describes the primary function of flippases?
Help in increasing lipid-protein interaction in the outer leaflet of the bilayer.
Move certain phospholipids from one leaflet of the membrane to another.
Localize more negatively charged membrane proteins in the lipid bilayer.
Cause uncoupling of v-SNARES and t-SNARES after fusion of incoming vesicle with the target membrane.
Mitotic cyclin-CDK activity peaks in the M phase. This is because
Mitotic cyclin is synthesized only in M phase.
The threshold level of mitotic cyclin accumulates only in late G2.
Cyclin subunit is activated by phoshorylation only in M phase.
The kinase subunit is activated by dephosphorylation only in M phase.
The gel to liquid crystalline phase transition temperature in phosphatidyl choline (PC) lipids composed of dioleocyl (DO), dipalmitoyl (DP), disteroyl (DS) and palmitoyl oleoyl (PO) fatty acids in increasing order will be
DOPC > DPPC > POPC > DSPC
DSPC > DPPC > POPC > DOPC
DPPC > DSPC > DOPC > POPC
POPC > DPPC > DOPC > DSPC
Which of the following is NOT an example of transmembrane transport between different subcellular compartments?
Transport from the cytoplasm into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
Transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex.
Transport from stroma into thylakoid space.
Transport from mitochondrial intermembrane space into the mitochondrial matrix.
Which of the following are NOT transcribed by RNA Polymerase II?
miRNA and some snRNA
miRNA and snoRNA
mRNA and snoRNA
tRNA and 5S rRNA
RNA editing, a post-transcriptional process, is achieved with the help of guide RNA (g-RNA). Which one of the following statements about the process is NOT true?
g-RNA dependent RNA editing happens in the kinetoplast DNA.
g-RNA is involved in chemical modification of t-RNA.
This process involves insertion or deletion of uridines.
Sequences edited once may be re-edited using a second g-RNA
