 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhat would be the effect on newt limb regeneration, if more than 90% of the nerve supply is severed before amputation?
The apical ectodermal cap stimulates growth of the blastema by secreting FGF8 but regeneration does not take place.
Limb regenration will take place and form a limb with no nerve supply.
Outgrowth will occur but the identity of the limb formed will be lost with no clear anterior-posterior polarity.
Limb regeneration with nerve supply will take place.
A.
The apical ectodermal cap stimulates growth of the blastema by secreting FGF8 but regeneration does not take place.
The effect on new limb regeneration will be that the apical ectodermal cap stimulates growth of the blastema by secreting FGF8 but regeneration does not take place.
Following are the events that might take place during dorso-ventral axis specification in early embryonic development of Drosophila:
A. 'Torpedo' receptor activation
B. 'Pipe' synthesis
C. A cascade of protease activity.
D. 'Cactus' dephosphorylation.
E. Entry of 'Dorsal' in the nuclei of syncytial blastoderm stage embryo.
Which combination of the above events will occur in the presumptive dorsal side of the embryo deficient in maternal gurken?
A only
B and C only
B, C, and E only
B, C, D, and E only
C. elegans embryo uses both autonomous and conditional modes of specification. Conditional specification. Conditional specification at the 4-cell stage can be seen in the development of the endoderm cell lineage and also in the establishment of dorsal-ventral axis. Following are few statements regarding this:
A. If the P2 cell is removed at the early 4-cell stage, the EMS cell will divide into two MS cells and no endoderm will be made.
B. In pop-1 deficient embryos, both EMS daughter cells become E cells.
C. When the position of ABa and ABp was reversed, their fates get reversed and no normal embryo forms.
D. In embryo whose mother have mutant glp-1, ABp is transformed into ABa cell.
Which of the above statements are true?
A, B, and D
A, B, and C
B, C, and D
A, C, and D
During vulva development in C.elegans, the anchor cell produces Lin-3 protein which interacts with the Let-23 protein present on the six vulval precursor cells (VPCs) that form an equivalence group. The central lineage cell (P6.p) adopts the primary fate, the adjacent VPCs (P5.p and P7.p) adopt the secondary fate and the rest VPCs adopt the tertiary fate. Few mutants (column A) and phenotypes (Column B) are listed in the table given below.
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Loss of function of lin-3 | i. P5.p, P6.p and P7.p adopt primary fate, P4.p and P8.p adopt secondary fate. |
| B. Loss of function of lin-3 and gain of function of let-23 | ii. Multivulva |
| C. Reduced function of lin-3. | iii. P6.p adopt primary fate and the rest of the VPCs adopt tertiary fate. |
| D. Overexpression of lin-3 | iv. All VPCs adopt tertiary fate |
Match the correct mutant with the observed phenotype.
A - iv; B - ii; C - iii; D - i
A - iv; B - iii; C - i; D - ii
A - ii; B - iii; C - iv; D - i
A - iii; B - i; C - ii; D - iv
Identification of genes that are associated with the development of male and/ or female gametophyte and embryogenesis in plants is facilitated by T-DNA mediated insertional mutagenesis. In an experiment, a transgenic plant was generated by insertion of T-DNA (containing a Kanamycin-resistance gene) into a gene "A". Self pollination of the T0 plant generated F1 progeny that segregated in a 2:1 ratio for resistance : sensitivity to Kanamycin. These observations indicate that
the mutant allele did not segregate from the wild type allele.
mutation in gene "A" induces lethality in the male gametophyte.
mutation in gene "A" induces lethality in the female gametophyte.
mutation in gene "A" induces zygotic lethality.
Oncogenic viruses could have either DNA or RNA genomes. Listed below are some oncogenic viruses (Column A), their genome types (Column B) and the cancers caused by these viruses (Column C).
| A | B | C |
| a. Hepatitis B | i. DNA | x. Burkitt's lymphoma |
| b. Epstein-Barr Virus | ii. RNA | y. T cell leukaemia |
| c. HTLV | z. Hepatocellular carcinoma |
Find out the correct combination.
(a) (i) (x); (b) (ii) (y); (c) (ii) (z)
(a) (ii) (y); (b) (i) (z); (c) (ii) (x)
(a) (ii) (y); (b) (ii) (z); (c) (i) (y)
(a) (i) (z); (b) (i) (x); (c) (ii) (y)
Major Histocompatibility complex(MHC) molecules are encoded by a cluster of genes called MHC locus. There are several reasons why an MHC molecule on the surface of a cell is important. Which one of the following reasons is INCORRECT?
To display self class I to demonstrate that the cell is normal and healthy.
To display foreign-peptide in class I to show that the cell is infected and to engage with T helper cells.
To display a self-peptide in class I and II to test developing T cells for autoreactivity.
To display a self-peptide in class I and II to maintain tolerance to self -proteins.
Several types of molecules including the transmembrane glycoproteins can function as matrix receptors and co-receptors. However, the principal receptors on animal cells for binding most extracellular matrix proteins are the integrins. Which of the following statements is NOT true for integrins?
Integrins are transmembrane linker proteins that link to the cytoskeleton.
An integrin molecule is composed of two non-covalently associated glycoprotein subunits α and β. Both subunits span the cell membrane, with short intracellular C-terminal tails and large N-terminal extracellular domains.
the extracellular portion of the integrin dimer binds to specific carbohydrate residues in extracellular matrix proteins.
The intracellular portion binds to a complex of proteins that form a linkage to the cytoskeleton.
Two important features which aid the development of a tumor and its metastasis are epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis. A student testes four cell lines to determine capability by checking the expression the expression of VEGF-A, TWIST and Cyclin D1. Which one of the following figures is most likely to exhibit the characteristics of a highly cancer cell?
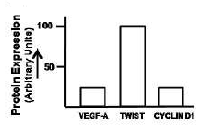
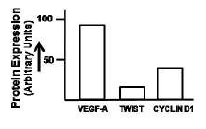
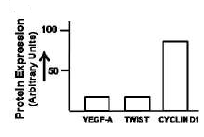
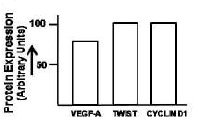
Two classes of genes - proto-oncogene and tumor suppressor gene usually contribute to the development of cancer. The following are some of the statements regarding both the genes.
A. Proto-oncogenes result in the development of cancer by gain-of-function mutation whereas tumor suppressor gene leads to cancer development by loss-of-function mutation.
B. Proto-oncogenes result in development in cancer by loss-of-function mutation whereas tumor suppressor gene leads to cancer development by gain-of-function mutation.
C. Mutation in both alleles of a protoncogene is required for induction of cancer whereas mutation in one of the two alleles in tumor suppressor gene is sufficient for promoting tumorigenesis.
D. Mutation in one of the two alleles in proto-oncogene is sufficient for induction of cancer whereas mutation in both the alleles of a tumor suppressor gene is required for promoting tumorigenesis.
Which combinations of the above statements are true for both the genes?
A and B
A and C
A and C
B and C
