 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA, B and C are the parallel sided transparent media of refractive indices n1 n2 and n3 respectively. They are arranged as shown in the figure. A ray is incident at an angle i on the surface of separation of A and B which is as shown in the figure. After the refraction into the medium B, the ray grazes the surface of separation of the madia B and C. Then, sin i equals to
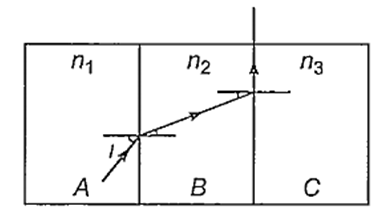
A.
Applying Snell's law between the surfaces A and B
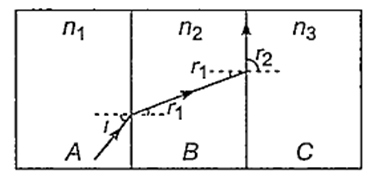
n1 sin i = n2 sin r1 ......(i)
Again applying Snell's law between surfaces B and C
n2 sin r1 = n3 sin r2 ...... (ii)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
A boat has green light of wavelength λ = 500 nm on the mast. What wavelength would be measured and what colour would be observed for this light as seen by a diver submerged in water by the side of the boat ? Given, .
Green of wavelength 376 nm
Red of wavelength 665 nm
Green of wavelength 500 nm
Blue of wavelength 376 nm
Two beams of red and violet colours are made to pass separately through a prism of A = 60°. In the minimum deviation position, the angle of refraction inside the prism will be
greater for red colour
equal but not 30° for both the colours
greater for violet colour
30° for both the colours
A plano-convex lens is made of refractive index of 1.6. The radius of curvature of the curved surface is 60 cm. The focal length of the lens is
400 cm
200 cm
100 cm
50 cm
The wavelength of the light used in Young's double slit experiment is λ. The intensity at a point on the screen is I, where the path difference is . IF I0 denotes the maximum intensity, then the ratio of I and I0 is
0.866
0.5
0.707
0.75
What is the minimum thickness of a thin film required for constructive interference in the reflected light from it ?Given, the refractive index of the film = 1.5, wavelength of the light incident on the film = 600 nm.
100 nm
300 nm
50 nm
200 nm
Critical angle for certain medium is sin-1 (0.6). The polarizing angle of that medium is
tan-1 (1.5)
sin-1 (0.8)
tan-1 (1.6667)
tan-1 (0.6667)
The spectrum of an oil flame is an example for
line emission spectrum
continuous emission spectrum
line absorption spectrum
band emission spectrum
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the graph of KE of the photoelectron emitted from the metal versus the frequency of the incident radiation gives a straight line graph, whose slope
depends on the intensity of the incident radiation
depends on the nature of the metal and also on the intensity of incident radiation
is same for all metals and independent of the intensity of the incident radiation
depends on the nature of the metal
An electron is moving in an orbit of a hydrogen atom from which there can be a maximum of six transition. An electron is moving in an orbit of another hydrogen atom from which there can be a maximum of three transition. The ratio of the velocities of the electron in these two orbits is
